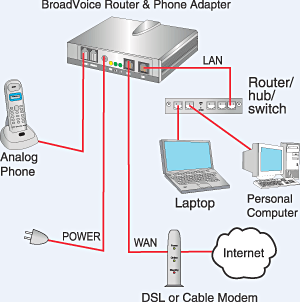
5.3.6: Internet Connections
- Page ID
- 22742
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Internet Access Technologies
There is a wide range of approaches to associate users and associations with the Internet.
Home clients (telecommuters) and workplaces regularly require an association with an Internet Service Provider (ISP) to access the Internet. Association alternatives change significantly among ISP and topographical areas. Notwithstanding, companies incorporate a broadband link, broadband computerized endorser line (DSL), remote WANs, and versatile administrations.
Associations commonly expect access to other corporate destinations and the Internet. Quick associations are required to help business administrations, including IP telephones, video conferencing, and server farm stockpiling.
Business-class interconnections are normally given by specialist organizations (SP). Well-known business-class administrations incorporate business DSL, rented lines, and Metro Ethernet.
Home and Small Office Internet Connections
Regular connection choices for little office and home office users:
- Cable: Typically offered by digital TV specialist co-ops, the Internet information signal is carried on a similar link that conveys satellite TV. It gives a high transmission capacity, consistently on, association with the Internet.
- DSL: Digital Subscriber Lines gives a high data transmission, consistently on, association with the Internet. DSL runs over a phone line when all is said in done, small office and home office clients associate utilizing Asymmetrical DSL (ADSL), which implies that the download speed is quicker than the upload speed.
- Cellular: For a Cell phone network to connect, it utilizes cellular internet access. Any place you can get a phone signal, you can get cell Internet. Execution will be restricted by the telephone's abilities and the cell tower to which it is associated. The fourth generation of broadband cellular network technology is 4G, which most people are familiar with because it is on smartphones. 5G is upcoming and expected to be faster than and succeed 4G by 100 times, which will have the ability to transmit a lot more data at a much faster pace than 4G.
- Satellite: Internet access through satellite is a genuine advantage in those territories that would somehow or another have no Internet availability by any means. Satellite dishes require a clear line of sight to the satellite.
- Dial-up telephone: An economical choice that utilizes any telephone line and a modem. The low transmission capacity supported by a dial-up modem association is normally not adequate for huge information transfer. However, it is still a valuable choice wherever other options are not available such as in rural areas or remote locations where phones are the only means of communication.
Fiber optic links are increasingly becoming more available to home and small businesses. This empowers an ISP to give higher data transmission speeds and bolster more administrations, for example, Internet, telephone, and TV.
Business Internet Connections
Corporate connection choices contrast from home client alternatives. Organizations may require higher transmission capacity, devoted data transmission, and oversaw administrations. Business connection options include:
- Dedicated Leased Line: Leased lines are really saved circuits inside the specialist organization's system that interface geologically isolated workplaces for private voice or potentially information organizing. The circuits are ordinarily leased at a month-to-month or yearly rate. They can be costly.
- Ethernet WAN: Ethernet WANs broaden LAN access into the WAN. Ethernet is a LAN innovation you will find out about in a later section. The advantages of Ethernet are currently being reached out into the WAN.
- DSL: Business DSL is accessible in different organizations. A famous decision is Symmetric Digital Subscriber Lines (SDSL) which is like the purchaser rendition of DSL. However, it gives transfers and downloads at similar paces.
- Satellite: Like small office and home office clients, satellite help can give an association when a wired arrangement isn't accessible.
The decision of connection shifts relying upon topographical area and specialist organization accessibility.
Wireless communications must adhere to regulations by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)Links to an external site. to avoid interference with other wireless transmission.

Radio antennas on Sandia Peak, New Mexico, by Maveric149m, Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license
Wireless LAN (WLAN) channels that support IEEE 802.11 protocols and equipment are typically sold under the trademark Wi-Fi. IEEE 802.11 protocols are the standard that allows two or more devices to communicate with each other without a wired connection.
Some standard frequency ranges:
Radio waves
The intended use is for a short distance, and devices transmit data in the frequency range of 30Khz to 300 GHz. Examples include cordless phones, radio stations, Bluetooth devices, garage openers, and GPS.
Microwave
Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through communication satellites. Communication satellites(CS) are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and government. A CS, known as Geostationary Satellite, comprises a transmitter of high-frequency radio waves in space, operates about 22,300 miles above the equator, and a receiver at different places, known as a satellite station on earth, as illustrated below. Nothing obstructs the radio waves between the transmitter and the receiver, or they must be in the line of sight.
How does satellite communication work?
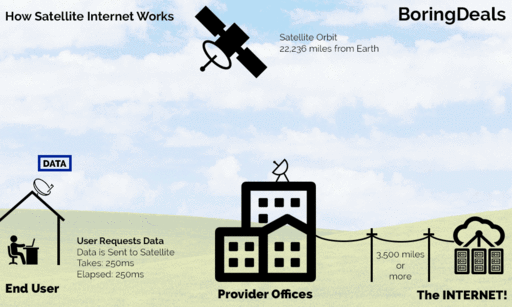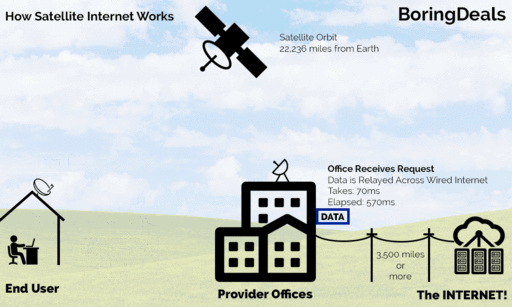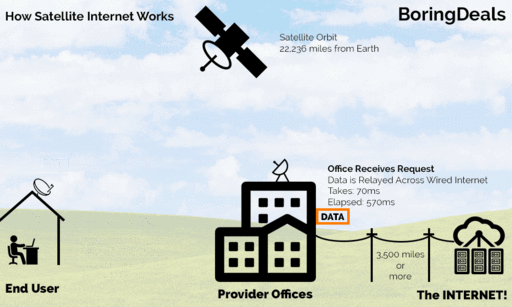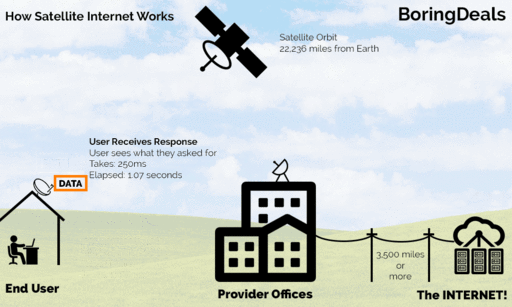
Animated Image of How Satellite Internet Works, by Vgeek15, Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license
What is Geostationary Satellite Transmission?
Satellites orbit above the earth and need to follow regulations of where they can circle to avoid interference with each other. Here is a brief description:
LEO (Low-Earth-Orbit) – 100 to 1000 miles out
-
- Used for wireless e-mail, special mobile telephones, pagers, spying, videoconferencing
MEO (Middle-Earth-Orbit) – 1000 to 22,300 miles
-
- Used for GPS (global positioning systems) and government
GEO (Geosynchronous-Earth-Orbit) – 22,300 miles
-
- Consistently over the same position on earth (and constantly over the equator)
- Used for weather, television, government operations
Watch a 1-min video explanation by Neil deGrasse Tyson describing the different types and their capabilities.
Fun fact: StarlinksLinks from SpaceX is an example of a satellite internet constellation. It provides Internet access to several countries. It consisted of over 3000 small satellites in low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Infrared frequencies
The signals are invisible to the human eye and operate from 300 GHz to 400 GHz. Examples include remote controls, electrical heaters, security systems, and pointing devices. While the waves are not visible to human eyes, the heating effect of infrared light can blind and cause burns to people.


