4.1.3: Categories of Software and Their Purposes
- Page ID
- 10104
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
- Identify the major categories of software and the purpose of each.
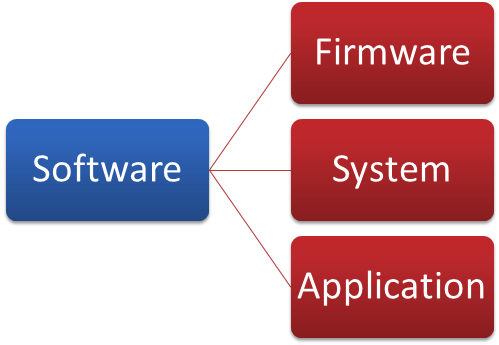
Categories of Software
There are three categories of software:
-
Firmware is software that has been permanently written on a read-only memory computer chip.
-
System software controls the loading of application programs and controls input and output to the computer.
-
Application software is the set of programs that the user manipulates to accomplish user-related tasks.
CC-BYby Janet Zimmer.
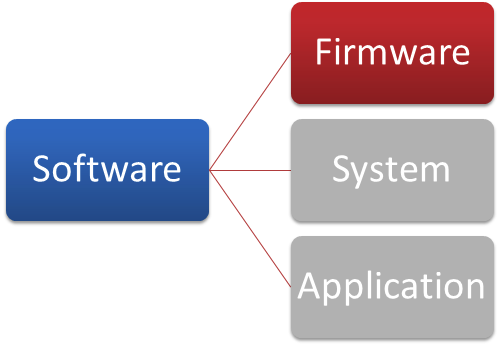
Firmware
Let's first take a look at firmware.
CC-BYby Janet Zimmer.
EXAMPLE
Title
Marcia has a standalone DVD player that she likes to take with her on trips. She sometimes purchases DVDs during a trip when she sees a movie that holds particular interest for her. When she took her first trip to Italy, she purchased such a movie. However, it would not play on her portable DVD player. The movies she brought with her from the States work just fine. Why will the one purchased in Italy not play?
The reason for Marcia's problem with the new movie purchased in Italy is that many standalone DVD players are sold with a region code built into the firmware in the player. Movies that do not have the same embedded region code will not play on the DVD player.
Like Marcia's DVD player, many items in your house, such as a "newer" washing machine, coffee brewer, television, or sound system, most likely have firmware embedded on a computer chip that controls some of the cycles or functions of the machine. Firmware is a type of program that is, for the most part, permanently embedded on a read-only memory (ROM), programmable read-only memory (PROM), or erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM) computer chip. In other words, firmware is a combination of hardware (the chip) and software (the program). But unlike the random access memory (RAM) chips in your computer, these programs are not lost or discarded when the machine is powered off. Unless the chips themselves fail because of damage to the chip hardware or its embedded circuits, the programs stay present on the chip.
As noted by the acronyms PROM and EPROM, sometimes the embedded software can be changed or updated. Why would you want to update firmware installed on a device? Perhaps the original version was found to have bugs or faults. Or it might be that the device, such as a DVD player or MP3 player, will not play a newer version of DVDs or music files that have newer security mechanisms embedded in the files. If there are no available upgrades to the firmware available, the only other option would be to replace the entire device in order to use the newer capabilities that are not compatible with an older version of the item.
Your computer contains firmware, both in the set of minimal instructions that allows your computer to load the operating system when you turn on the machine, and in other devices such as the optical drive (DVD/CD player) and the hard drive. An operating system is stored on the hard drive on your computer. Without that simple set of instructions in firmware, your computer would not boot up—that is, it would not load the operating system from the hard drive when you press the ON switch.
So think of firmware as software that is more or less permanently written to hardware (the chips) and that performs relatively less complex but still critical functions. Because there are no standardized mechanisms for determining what version of firmware has been installed on a particular device, firmware is hardly ever (with the exceptions noted below) automatically updated with downloads via the internet, unlike updates to your operating system or security files that you can automatically download when you are connected to the internet. There are websites, however, that provide instructions on how to look for updated versions of the firmware that is installed on many devices. And some devices, such as newer cell phones, allow the owner to update firmware by connecting wirelessly to the provider's website. It is even possible for Marcia to unlock the region code on her DVD player so that it will play movies made and sold in any part of the world.
did I get this
True or false? If the device is controlled by a firmware chip and the electronic components (circuits) on the chip fail, the only option is to replace the chip (or potentially the entire device).
True or false? If the device is controlled by a firmware chip and the device no longer works because the firmware is out of date, the only option is to replace the chip or the entire device.
Reset this Activity
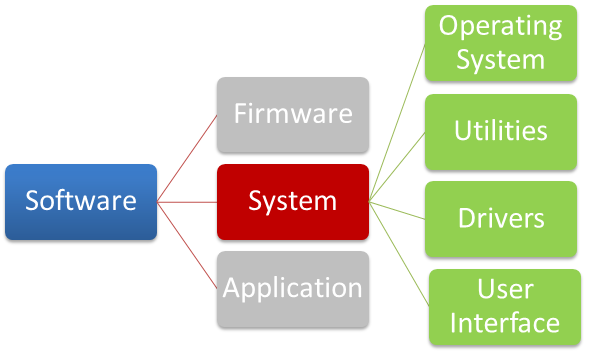
System Software—Operating System and Utility Programs
System software consists of operating systems, utility programs, device drivers, and the user interface (UI).
CC-BYby Janet Zimmer.
We will be taking a much closer look at the operating system (OS) in the next module. For now, consider that the operating system is the interface between the user and the computer hardware. It coordinates the working of the pieces of the system unit discussed in unit 2, Understanding the Computer System Unit, things such as the CPU, memory, and the hard drive. In addition, the operating system keeps track of files, determines the order in which tasks are accomplished, controls access to input and output devices, and provides a level of security via access to the computer system itself (logon procedures).
System software also includes device drivers and utility programs. Your touch screen, mouse, keyboard, monitor, USB port, and other peripheral devices communicate with you and the computer via special software called device drivers. Many items that are part of the system unit come with device drivers already installed. Today, even components that you might add to your system unit, internal or external, are considered "plug and play," which means as soon as you connect the item, the driver automatically is loaded. In some cases, however, you have to download a driver or install it via CD or DVD.
The basic utility programs that come installed with any operating system on a computer include software that will do a backup of your programs and files and allow for recovery of those programs and files; a hard disk defragger, which eliminates gaps that occur when files are stored in different segments of the hard drive; a program that scans the entire hard disk and removes unnecessary files, such as temporary files; and a compression utility that will compress files to make them take up less space on the hard drive.
Operating systems found on mobile devices such as smartphones have a somewhat smaller subset of the system software and utility programs as those found on a computer.
The user interface, what you see on the screen, is also part of the operating system. Each OS has its own look and feel in the way it presents lists or icons that a user clicks on to perform tasks or open programs or files. Personal computers with operating systems such as Windows or Macintosh (Mac OS) implement a GUI (graphical user interface). A user can modify the way the user interface looks, but interaction is typically via icons and menus. UNIX and systems running MS-DOS may use a command-line interface where each command is typed on the screen, versus using a mouse click to initiate an action.
learn by doing
New Section Title
Which of the following isnota function provided by the operating system or utility programs?
Reset this Activity
You have purchased a new digital camera and are downloading to your computer special software that allows your computer to recognize the camera when the two are joined via a cable. This type of software is considered .
Reset this Activity
True or false? System software consists of an operating system. Other software is either firmware or application software.
Libraries of functions and drivers for printers and other hardware belongs in the category of .
Reset this Activity
Tracy really likes the new touch-screen tablets that allow you to manage the screen activities using a swipe of your fingers. This new technology belongs to the category of which type of software?
Reset this Activity
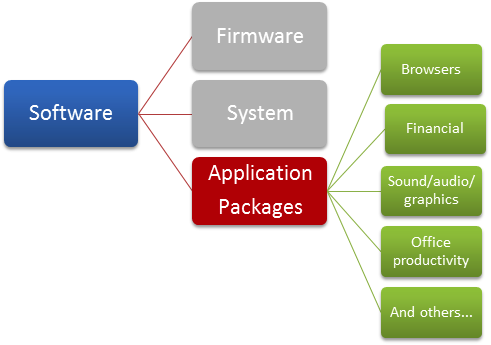
Application Software
CC-BYby Janet Zimmer.
As with the OS, we will look at application software in greater detail in a later module. Application software packages (apps) consist of software programs that the user manipulates to accomplish computer-related tasks. A partial list of categories of applications or packages for computers would include web browsers, office suites (for word processing, spreadsheets, databases, presentations), sound/music file manipulation software, audio and video file manipulation software, games, graphic file manipulation software, and financial or accounting software. There are special application packages available for mobile devices as well.
Application software is installed separately from the operating system and often must be purchased separately. Some application software may come already pre-installed on the computer, but frequently, users must install particular applications after purchase. We will address platform compatibility issues, memory requirements, and appropriate licenses in the module on software applications.
learn by doing
New Section Title
When you use your computer to write a research paper for your class, which types of software are you using? Select Yes or No for each option.
Firmware
Operating system
Application
Reset this Activity
True or false? Software application packages can function independently of an operating system.
Reset this Activity
Application software is a term used for any software that runs a program. Strictly speaking, then, operating systems and utilities are types of application software. In the context of this course, however, application software refers to __________.
Reset this Activity

