1.4: Components of a Computer
- Page ID
- 13560
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The next few pages describe all of the components that make up a computer. While computers do come in various sizes and shapes, they all share common attributes to function.
Computer Case

The computer case is the metal and plastic box that contains the main components of the computer, including the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), and power supply. The front of the case usually has an On/Off button and one or more optical drives.
Computer cases come in different shapes and sizes. A desktop case lies flat on a desk, and the monitor usually sits on top of it. A tower case is tall and sits next to the monitor or on the floor. All-inone computers come with the internal components built into the monitor, which eliminates the need for a separate case.
Computer Monitor
 Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NCThe monitor works with a video card, located inside the computer case, to display images and text on the screen. Most monitors have control buttons that allow you to change your monitor's display settings, and some monitors also have built-in speakers.
Keyboard & Mouse

The keyboard is one of the main ways to communicate with a computer. There are many different types of keyboards, but most allow you to accomplish the same basic tasks. The mouse is another important tool for communicating with computers. A computer mouse functions as a pointing device on the screen allowing the user to select and manipulate objects.
Motherboard
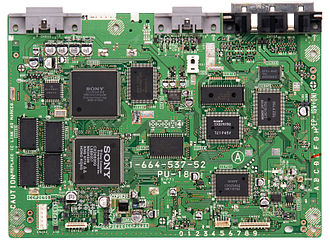
If a computer were a human being, the motherboard would be the spinal cord. The motherboard is a thin circuit board that connects all of the elements of a computer together. Examples of items connected to the motherboard include the CPU, memory, connectors for the hard drive and optical drives, expansion cards to control the video and audio, and connections to your computer's ports (such as USB ports). The motherboard connects directly or indirectly to every part of the computer.
CPU/Processor

Continuing the human being analogy, if a computer were a person, the central processing unit (CPU), also called a processor, would be the brain. The CPU is located inside the computer case and is situated on the. The job of a CPU is to carry out commands. Whenever you press a key, click the mouse, or start an application, you're sending instructions to the CPU.
The CPU is usually a two-inch ceramic square with a silicon chip located inside. The chip is usually about the size of a thumbnail. The CPU fits into the motherboard's CPU socket, which is covered by the heat sink, an object that absorbs heat from the CPU and usually a fan. A CPU can be cooled passively through just the heat sink, through a fan, or liquid-cooled.
A processor's speed is measured in megahertz (MHz), or millions of instructions per second; and gigahertz (GHz), or billions of instructions per second. A faster processor can execute instructions more quickly. However, the actual speed of the computer depends on the speed of many different components—not just the processor.
RAM (Random Access Memory)

RAM is your system's short-term memory. Whenever your computer performs calculations, it temporarily stores the data in the RAM. The system retrieves the information to be sent to the processor or other components when needed. Ram only provides temporary storage when the computer is off, all of the information stored in Ram is erased. RAM is measured in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB). The higher the RAM, the more applications and programs that can be run and executed at the same time. One of the fastest ways to speed up a sluggish system is to add more RAM.
Hard Drive
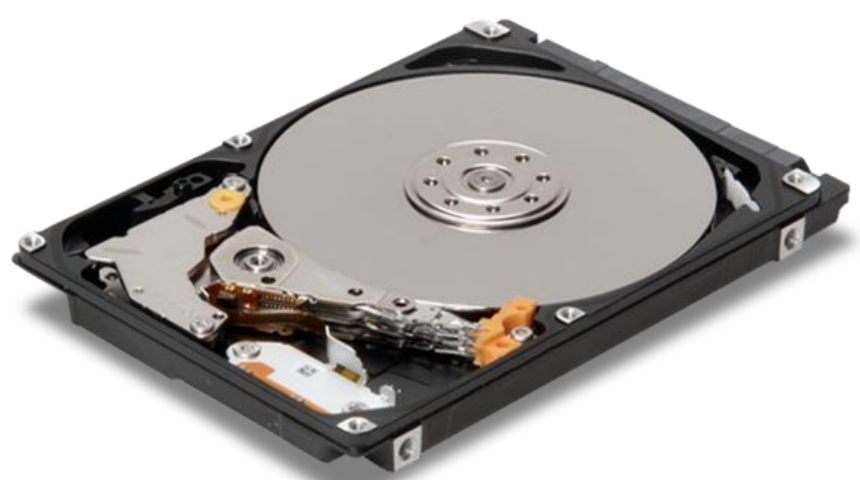

The Hard Drive is your computer’s long term memory. The data is also persistent, which means that the information is stored on the drive even when there is no power to the drive. The hard drive is where your software, documents, and other files are stored. The faster the hard drive, the faster your computer can start up and load programs.
Power Supply

The power supply unit in a computer converts the power from the wall outlet (AC) to the type of power needed by the computer (DC). It sends power through cables to the motherboard and other components and also ensures that the power is regular and reliable.
Expansion Cards (Video card, Sound card, Network Card, etc.
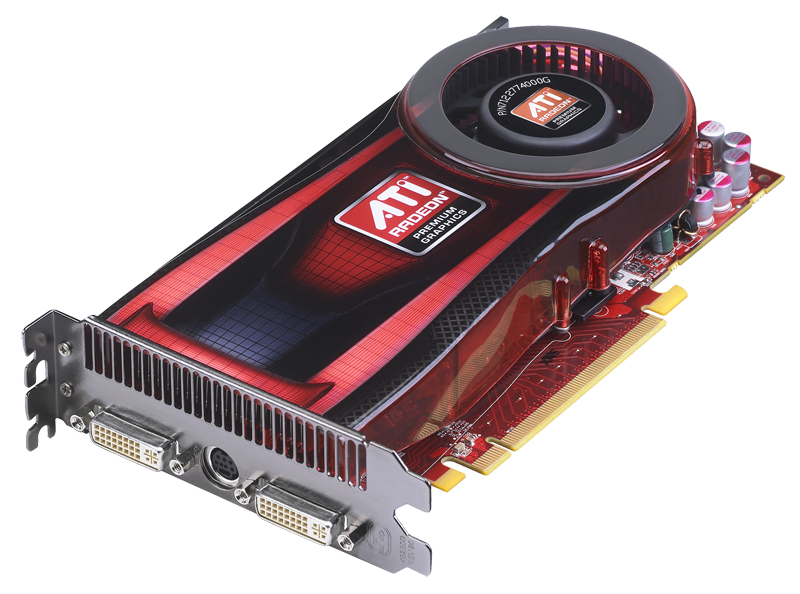

Some computers can be expanded or upgraded. Desktop computers often have expansion slots on the motherboard that allow various types of expansion cards to be added for a fast connection to the CPU. These expansion cards are called PCI (peripheral component interconnect) cards. Adding cards could increase the quality or performance of the software used on a computer. Video editors, for example, install a powerful graphics card to aid them in their editing work.


