3.1: Introduction
- Page ID
- 3927
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)To build an effective emergency management organization, it is necessary to understand the relationships among some of the stakeholders that are involved. As noted in Figure 2-1, local government has downward vertical linkages with households and businesses, upward vertical linkages with state and federal agencies, and horizontal linkages with social and economic influentials and hazards practitioners. However, it also is important to understand the horizontal and vertical linkages within local government. Specifically, local emergency management agencies (LEMAs) typically have horizontal linkages with personnel in police, fire, emergency medical services, public works, and emergency management/homeland security departments. At the municipal level, all of these departments report to (i.e., have a vertical linkage with) their jurisdiction’s chief administrative officer (CAO), such as a mayor or city manager, who has direct supervisory authority over them. The CAO is responsible for ensuring these departments perform their assigned duties within the requirements of the law and accomplish these functions within the time and funds allocated to them. Accordingly, the CAO has the authority to hire, fire, allocate funds, and evaluate performance—a relationship represented in Figure 3-1 as a solid line. However, the CAO typically is not an expert in public safety, emergency medicine, or emergency management and, therefore, cannot provide these departments with guidance on how to perform their missions most effectively. Thus, city and county agencies frequently have vertical linkages with corresponding agencies at the state (and sometimes federal) level that provide technical, and sometimes financial, assistance. Because agencies at higher (state and federal) levels of government lack the legal authority to compel performance by the corresponding agencies at lower (county and city) levels, their relationship is sometimes represented as a “dotted line” relationship in organizational charts (see Figure 3-1). In turn, the agencies at the state level report to the governor in a line relationship just as the agencies at the local level report to their jurisdictions’ CAOs.
The relationships among agencies at the county level are somewhat more complex for jurisdictions in which agency heads are directly elected by the voters rather than appointed by the local CAO. County sheriffs, in particular, can be quite protective of their autonomy, so they can be characterized as having just as much of a “dotted line” relationship with the Chair of the County Board of Supervisors as with the state police.
Although it is not shown in Figure 3-1, the hierarchical relationship between the local and state levels also extends to the federal level, with the corresponding agencies represented at each level. In addition, however, emergency management organizations have two other “dotted line” relationships that should be noted. First, local emergency managers often establish memoranda of agreement (MOA) with peer agencies in neighboring jurisdictions to provide personnel and material support during emergencies. Second, emergency management agencies have close relationships with Local Emergency Management Committees (LEMCs), which is a generic term for formalized disaster planning networks that are used to increase coordination among emergency-relevant agencies within a given community.
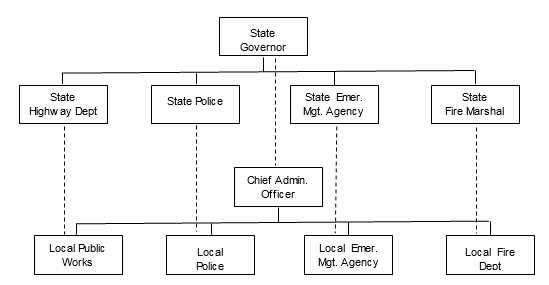
Figure \( \PageIndex{1} \): Relationships among local and state agencies
Some of these LEMCs are established by legal mandate, as is the case for those required by the Emergency Planning and Community Right to Know Act (also known as the Title III of the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986—SARA Title III) to inform and prepare their communities for accidental releases of toxic chemicals. However, some emergency managers have established similar organizations without a specific legal mandate—calling them disaster preparedness committees, disaster planning committees, emergency management advisory committees, or some other similar name (Daines, 1991; Drabek, 1987, 1990). Some of these LEMCs have assumed responsibility for disaster recovery and hazard mitigation as well as preparedness and response, and some address all hazards to which their community is exposed, not just accidental releases of toxic chemicals. Although LEPCs established under SARA Title III are probably the most common of these emergency planning organizations and LEPCs have been the subject of more research than any other type of formalized planning network, the lessons learned from studies of LEPCs are likely to apply to all such organizations. Consequently, we will use the more generally applicable acronym LEMC throughout the remainder of this book.

