18.5: Function Library Group
- Page ID
- 13702
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)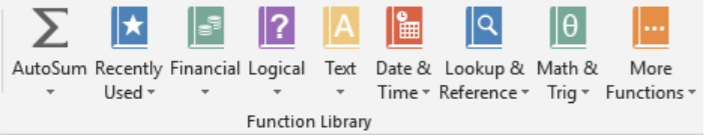
The Function Library Group allows the user to utilize all of the formulas in Excel. The function is automatically inserted in the cell that is selected.
Auto Sum
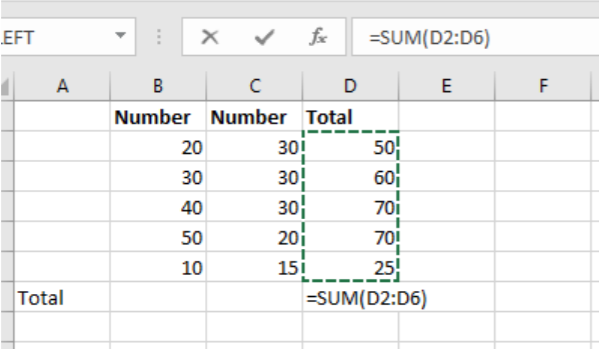
 The first icon on the left is AutoSum. Autosum adds multiple cells together. After selecting Autosum, Excel intelligently guesses the range for your calculation based upon the cells around the insertion point. The user can change the cell location in the address bar.
The first icon on the left is AutoSum. Autosum adds multiple cells together. After selecting Autosum, Excel intelligently guesses the range for your calculation based upon the cells around the insertion point. The user can change the cell location in the address bar.
If the user wants other frequently used commands for multiple cells, they can select the more options arrow next to Autosum. A list of options will generate.
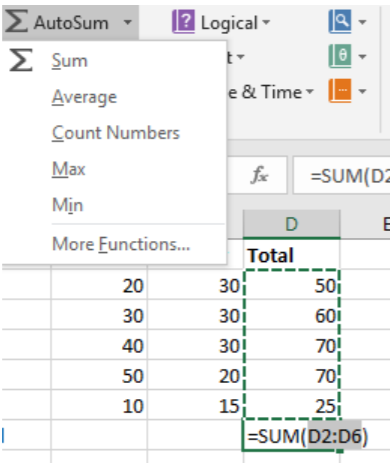
Average calculates the sum of all the selected cells divided by the number of cells selected to find the average. Count Numbers allows the user to quickly calculate the number of cells included. Max determines the largest number in the group, and Min calculates the smallest number. More Functions launches the Functions Arguments box to allow for more options to search for a function in all categories of Excel.
Recently Used
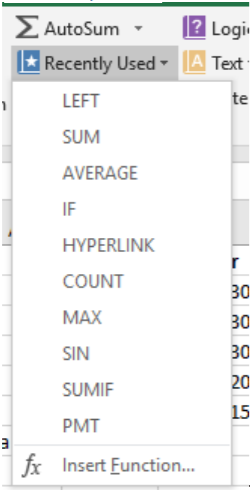
The recently used icon allows the user to select functions they have used most recently in Excel. This is especially helpful when performing similar calculations.
Financial
 Financial functions are used to calculate business equations such as interest, depreciation, and valuation. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
Financial functions are used to calculate business equations such as interest, depreciation, and valuation. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Financial | Function Description |
|---|---|
| ACCRINT function | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest |
| ACCRINTM function | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity |
| AMORDEGRC function | Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient |
| AMORLINC function | Returns the depreciation for each accounting period |
| COUPDAYBS function | Returns the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to the settlement date |
| COUPDAYS function | Returns the number of days in the coupon period that contains the settlement date |
| COUPDAYSNC function | Returns the number of days from the settlement date to the next coupon date |
| COUPNCD function | Returns the next coupon date after the settlement date |
| COUPNUM function | Returns the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and maturity date |
| COUPPCD function | Returns the previous coupon date before the settlement date |
| CUMIPMT function | Returns the cumulative interest paid between two periods |
| CUMPRINC function | Returns the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods |
| DB function | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the fixed-declining balance method |
| DDB function | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the double-declining balance method or some other method that you specify |
| DISC function | Returns the discount rate for a security |
| DOLLARDE function | Converts a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number |
| DOLLARFR function | Converts a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a dollar price, expressed as a fraction |
| DURATION function | Returns the annual duration of a security with periodic interest payments |
| EFFECT function | Returns the effective annual interest rate |
| FV function | Returns the future value of an investment |
| FVSCHEDULE function | Returns the future value of an initial principal after applying a series of compound interest rates |
| INTRATE function | Returns the interest rate for a fully invested security |
| IPMT function | Returns the interest payment for an investment for a given period |
| IRR function | Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
| ISPMT function | Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment |
| MDURATION function | Returns the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed par value of $100 |
| MIRR function | Returns the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows are financed at different rates |
| NOMINAL function | Returns the annual nominal interest rate |
| NPER function | Returns the number of periods for an investment |
| NPV function | Returns the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate |
| ODDFPRICE function | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first period |
| ODDFYIELD function | Returns the yield of a security with an odd first period |
| ODDLPRICE function | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last period |
| ODDLYIELD function | Returns the yield of a security with an odd last period |
PDURATION function  |
Returns the number of periods required by an investment to reach a specified value |
| PMT function | Returns the periodic payment for an annuity |
| PPMT function | Returns the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period |
| PRICE function | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic interest |
| PRICEDISC function | Returns the price per $100 face value of a discounted security |
| PRICEMAT function | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest at maturity |
| PV function | Returns the present value of an investment |
| RATE function | Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity |
| RECEIVED function | Returns the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security |
RRI function  |
Returns an equivalent interest rate for the growth of an investment |
| SLN function | Returns the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period |
| SYD function | Returns the sum-of-years' digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period |
| TBILLEQ function | Returns the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill |
| TBILLPRICE function | Returns the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill |
| TBILLYIELD function | Returns the yield for a Treasury bill |
| VDB function | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period by using a declining balance method |
| XIRR function | Returns the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
| XNPV function | Returns the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
| YIELD function | Returns the yield on a security that pays periodic interest |
| YIELDDISC function | Returns the annual yield for a discounted security; for example, a Treasury bill |
| YIELDMAT function | Returns the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity |
Logical Functions
 Logical functions are used to compared data in different cells. Depending on the logical functions used, excel populates the cell with the logical formula as TRUE or FALSE depending on the calculation of the formula. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
Logical functions are used to compared data in different cells. Depending on the logical functions used, excel populates the cell with the logical formula as TRUE or FALSE depending on the calculation of the formula. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Logical Function | Description |
|---|---|
| AND function | Returns TRUE if all of its arguments are TRUE |
| FALSE function | Returns the logical value FALSE |
| IF function | Specifies a logical test to perform |
| IFERROR function | Returns a value you specify if a formula evaluates to an error; otherwise, returns the result of the formula |
IFNA function  |
Returns the value you specify if the expression resolves to #N/A, otherwise returns the result of the expression |
IFS function  |
Checks whether one or more conditions are met and returns a value that corresponds to the first TRUE condition. |
| NOT function | Reverses the logic of its argument |
| OR function | Returns TRUE if any argument is TRUE |
SWITCH function  |
Evaluates an expression against a list of values and returns the result corresponding to the first matching value. If there is no match, an optional default value may be returned. |
| TRUE function | Returns the logical value TRUE |
XOR function  |
Returns a logical exclusive OR of all arguments |
Text Functions
 Text functions are powerful components of Excel that convert numbers into letters and can also remove or copy letters or numbers from other cells into the current cell. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
Text functions are powerful components of Excel that convert numbers into letters and can also remove or copy letters or numbers from other cells into the current cell. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Text Function | Description |
|---|---|
| ASC function | Changes full-width (double-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to half-width (single-byte) characters |
| BAHTTEXT function | Converts a number to text, using the ß (baht) currency format |
| CHAR function | Returns the character specified by the code number |
| CLEAN function | Removes all nonprintable characters from text |
| CODE function | Returns a numeric code for the first character in a text string |
CONCAT function  |
Combines the text from multiple ranges and/or strings, but it doesn't provide the delimiter or IgnoreEmpty arguments. |
| CONCATENATE function | Joins several text items into one text item |
DBCS function  |
Changes half-width (single-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to full-width (double-byte) characters |
| DOLLAR function | Converts a number to text, using the $ (dollar) currency format |
| EXACT function | Checks to see if two text values are identical |
| FIND, FINDB functions | Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive) |
| FIXED function | Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals |
| LEFT, LEFTB functions | Returns the leftmost characters from a text value |
| LEN, LENB functions | Returns the number of characters in a text string |
| LOWER function | Converts text to lowercase |
| MID, MIDB functions | Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify |
NUMBERVALUE function  |
Converts text to number in a locale-independent manner |
| PHONETIC function | Extracts the phonetic (furigana) characters from a text string |
| PROPER function | Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value |
| REPLACE, REPLACEB functions | Replaces characters within text |
| REPT function | Repeats text a given number of times |
| RIGHT, RIGHTB functions | Returns the rightmost characters from a text value |
| SEARCH, SEARCHB functions | Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive) |
| SUBSTITUTE function | Substitutes new text for old text in a text string |
| T function | Converts its arguments to text |
| TEXT function | Formats a number and converts it to text |
TEXTJOIN function  |
Combines the text from multiple ranges and/or strings, and includes a delimiter you specify between each text value that will be combined. If the delimiter is an empty text string, this function will effectively concatenate the ranges |
| TRIM function | Removes spaces from text |
UNICHAR function  |
Returns the Unicode character that is referenced by the given numeric value |
UNICODE function  |
Returns the number (code point) that corresponds to the first character of the text |
Date & Time Function
 Date & Time functions calculate numbers into dates. There are many options available to return the date as desired from a variety of data sets. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
Date & Time functions calculate numbers into dates. There are many options available to return the date as desired from a variety of data sets. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Date & Time Function | Description |
|---|---|
| DATE function | Returns the serial number of a particular date |
| DATEDIF function | Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. This function is useful in formulas where you need to calculate an age. |
| DATEVALUE function | Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number |
| DAY function | Converts a serial number to a day of the month |
DAYS function  |
Returns the number of days between two dates |
| DAYS360 function | Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
| EDATE function | Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date |
| EOMONTH function | Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months |
| HOUR function | Converts a serial number to an hour |
ISOWEEKNUM function  |
Returns the number of the ISO week number of the year for a given date |
| MINUTE function | Converts a serial number to a minute |
| MONTH function | Converts a serial number to a month |
| NETWORKDAYS function | Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates |
NETWORKDAYS.INTL function  |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
| NOW function | Returns the serial number of the current date and time |
| SECOND function | Converts a serial number to a second |
| TIME function | Returns the serial number of a particular time |
| TIMEVALUE function | Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number |
| TODAY function | Returns the serial number of today's date |
| WEEKDAY function | Converts a serial number to a day of the week |
| WEEKNUM function | Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year |
| WORKDAY function | Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays |
WORKDAY.INTL function  |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
| YEAR function | Converts a serial number to a year |
| YEARFRAC function | Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date |
Lookup & Reference Formulas
 Lookup and Reference formulas allow you to work with large sets of data, and especially useful when you need to reference between multiple data sets. They can provide information about a range of data, find the location of a given address or value, or look up certain values in a large set of data. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
Lookup and Reference formulas allow you to work with large sets of data, and especially useful when you need to reference between multiple data sets. They can provide information about a range of data, find the location of a given address or value, or look up certain values in a large set of data. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Lookup & Reference Function | Description |
|---|---|
| ADDRESS function | Returns a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet |
| AREAS function | Returns the number of areas in a reference |
| CHOOSE function | Chooses a value from a list of values |
| COLUMN function | Returns the column number of a reference |
| COLUMNS function | Returns the number of columns in a reference |
FILTER function  |
Filters a range of data based on criteria you define |
FORMULATEXT function  |
Returns the formula at the given reference as text |
| GETPIVOTDATA function | Returns data stored in a PivotTable report |
| HLOOKUP function | Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell |
| HYPERLINK function | Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet |
| INDEX function | Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array |
| INDIRECT function | Returns a reference indicated by a text value |
| LOOKUP function | Looks up values in a vector or array |
| MATCH function | Looks up values in a reference or array |
| OFFSET function | Returns a reference offset from a given reference |
| ROW function | Returns the row number of a reference |
| ROWS function | Returns the number of rows in a reference |
| RTD function | Retrieves real-time data from a program that supports COM automation |
SORT function  |
Sorts the contents of a range or array |
SORTBY function  |
Sorts the contents of a range or array based on the values in a corresponding range or array |
| TRANSPOSE function | Returns the transpose of an array |
UNIQUE function  |
Returns a list of unique values in a list or range |
| VLOOKUP function | Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell |
XLOOKUP function  |
Searches a range or an array, and returns an item corresponding to the first match it finds. If a match doesn't exist, then XLOOKUP can return the closest (approximate) match. |
XMATCH function  |
Returns the relative position of an item in an array or range of cells. |
Math & Trig Function
 The Excel Math & Trig functions allow the user to perform mathematical equations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as trigonometry. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
The Excel Math & Trig functions allow the user to perform mathematical equations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as trigonometry. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Math & Trig Function | Description |
|---|---|
| ABS function | Returns the absolute value of a number |
| ACOS function | Returns the arccosine of a number |
| ACOSH function | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
ACOT function  |
Returns the arccotangent of a number |
ACOTH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic arccotangent of a number |
| AGGREGATE function | Returns an aggregate in a list or database |
| ARABIC function | Converts a Roman number to Arabic, as a number |
| ASIN function | Returns the arcsine of a number |
| ASINH function | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
| ATAN function | Returns the arctangent of a number |
| ATAN2 function | Returns the arctangent from x- and y-coordinates |
| ATANH function | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
BASE function  |
Converts a number into a text representation with the given radix (base) |
| CEILING function | Rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
CEILING.MATH function  |
Rounds a number up, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| CEILING.PRECISE function | Rounds a number the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded up. |
| COMBIN function | Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects |
COMBINA function  |
Returns the number of combinations with repetitions for a given number of items |
| COS function | Returns the cosine of a number |
| COSH function | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
COT function  |
Returns the cotangent of an angle |
COTH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic cotangent of a number |
CSC function  |
Returns the cosecant of an angle |
CSCH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of an angle |
DECIMAL function  |
Converts a text representation of a number in a given base into a decimal number |
| DEGREES function | Converts radians to degrees |
| EVEN function | Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer |
| EXP function | Returns e raised to the power of a given number |
| FACT function | Returns the factorial of a number |
| FACTDOUBLE function | Returns the double factorial of a number |
| FLOOR function | Rounds a number down, toward zero |
FLOOR.MATH function  |
Rounds a number down, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| FLOOR.PRECISE function | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded down. |
| GCD function | Returns the greatest common divisor |
| INT function | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer |
ISO.CEILING function  |
Returns a number that is rounded up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| LCM function | Returns the least common multiple |
| LN function | Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
| LOG function | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base |
| LOG10 function | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number |
| MDETERM function | Returns the matrix determinant of an array |
| MINVERSE function | Returns the matrix inverse of an array |
| MMULT function | Returns the matrix product of two arrays |
| MOD function | Returns the remainder from division |
| MROUND function | Returns a number rounded to the desired multiple |
| MULTINOMIAL function | Returns the multinomial of a set of numbers |
MUNIT function  |
Returns the unit matrix or the specified dimension |
| ODD function | Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer |
| PI function | Returns the value of pi |
| POWER function | Returns the result of a number raised to a power |
| PRODUCT function | Multiplies its arguments |
| QUOTIENT function | Returns the integer portion of a division |
| RADIANS function | Converts degrees to radians |
| RAND function | Returns a random number between 0 and 1 |
RANDARRAY function  |
Returns an array of random numbers between 0 and 1. However, you can specify the number of rows and columns to fill, minimum and maximum values, and whether to return whole numbers or decimal values. |
| RANDBETWEEN function | Returns a random number between the numbers you specify |
| ROMAN function | Converts an Arabic numeral to Roman, as text |
| ROUND function | Rounds a number to a specified number of digits |
| ROUNDDOWN function | Rounds a number down, toward zero |
| ROUNDUP function | Rounds a number up, away from zero |
SEC function  |
Returns the secant of an angle |
SECH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic secant of an angle |
| SERIESSUM function | Returns the sum of a power series based on the formula |
SEQUENCE function  |
Generates a list of sequential numbers in an array, such as 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| SIGN function | Returns the sign of a number |
| SIN function | Returns the sine of the given angle |
| SINH function | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
| SQRT function | Returns a positive square root |
| SQRTPI function | Returns the square root of (number * pi) |
| SUBTOTAL function | Returns a subtotal in a list or database |
| SUM function | Adds its arguments |
| SUMIF function | Adds the cells specified by a given criteria |
SUMIFS function  |
Adds the cells in a range that meet multiple criteria |
| SUMPRODUCT function | Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array components |
| SUMSQ function | Returns the sum of the squares of the arguments |
| SUMX2MY2 function | Returns the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
| SUMX2PY2 function | Returns the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
| SUMXMY2 function | Returns the sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two arrays |
| TAN function | Returns the tangent of a number |
| TANH function | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| TRUNC function | Truncates a number to an integer |
Statistical Functions
Statistical Functions are responsible for statistical analysis calculating items like mean, median, mode, etc. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Statistical Function | Description |
|---|---|
| AVEDEV function | Returns the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean |
| AVERAGE function | Returns the average of its arguments |
| AVERAGEA function | Returns the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| AVERAGEIF function | Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all the cells in a range that meet a given criteria |
AVERAGEIFS function  |
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all cells that meet multiple criteria |
BETA.DIST function  |
Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
BETA.INV function  |
Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
BINOM.DIST function  |
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
BINOM.DIST.RANGE function  |
Returns the probability of a trial result using a binomial distribution |
BINOM.INV function  |
Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
CHISQ.DIST function  |
Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
CHISQ.DIST.RT function  |
Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
CHISQ.INV function  |
Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
CHISQ.INV.RT function  |
Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
CHISQ.TEST function  |
Returns the test for independence |
CONFIDENCE.NORM function  |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
CONFIDENCE.T function  |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean, using a Student's t distribution |
| CORREL function | Returns the correlation coefficient between two data sets |
| COUNT function | Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments |
| COUNTA function | Counts how many values are in the list of arguments |
| COUNTBLANK function | Counts the number of blank cells within a range |
| COUNTIF function | Counts the number of cells within a range that meet the given criteria |
COUNTIFS function  |
Counts the number of cells within a range that meet multiple criteria |
COVARIANCE.P function  |
Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
COVARIANCE.S function  |
Returns the sample covariance, the average of the products deviations for each data point pair in two data sets |
| DEVSQ function | Returns the sum of squares of deviations |
EXPON.DIST function  |
Returns the exponential distribution |
F.DIST function  |
Returns the F probability distribution |
F.DIST.RT function  |
Returns the F probability distribution |
F.INV function  |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
F.INV.RT function  |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
F.TEST function  |
Returns the result of an F-test |
| FISHER function | Returns the Fisher transformation |
| FISHERINV function | Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation |
| FORECAST function | Returns a value along with a linear trend Note: In Excel 2016, this function is replaced with FORECAST.LINEAR as part of the new Forecasting functions, but it's still available for compatibility with earlier versions. |
FORECAST.ETS function  |
Returns a future value based on existing (historical) values by using the AAA version of the Exponential Smoothing (ETS) algorithm |
FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT function  |
Returns a confidence interval for the forecast value at the specified target date |
FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function  |
Returns the length of the repetitive pattern Excel detects for the specified time series |
FORECAST.ETS.STAT function  |
Returns a statistical value as a result of time series forecasting |
FORECAST.LINEAR function  |
Returns a future value based on existing values |
| FREQUENCY function | Returns a frequency distribution as a vertical array |
GAMMA function  |
Returns the Gamma function value |
GAMMA.DIST function  |
Returns the gamma distribution |
GAMMA.INV function  |
Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
| GAMMALN function | Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
GAMMALN.PRECISE function  |
Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
GAUSS function  |
Returns 0.5 less than the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| GEOMEAN function | Returns the geometric mean |
| GROWTH function | Returns values along an exponential trend |
| HARMEAN function | Returns the harmonic mean |
| HYPGEOM.DIST function | Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
| INTERCEPT function | Returns the intercept of the linear regression line |
| KURT function | Returns the kurtosis of a data set |
| LARGE function | Returns the k-th largest value in a data set |
| LINEST function | Returns the parameters of a linear trend |
| LOGEST function | Returns the parameters of an exponential trend |
LOGNORM.DIST function  |
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
LOGNORM.INV function  |
Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution |
| MAX function | Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments |
| MAXA function | Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
MAXIFS function  |
Returns the maximum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria |
| MEDIAN function | Returns the median of the given numbers |
| MIN function | Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments |
| MINA function | Returns the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| MINIFS function | Returns the minimum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria. |
MODE.MULT function  |
Returns a vertical array of the most frequently occurring, or repetitive values in an array or range of data |
MODE.SNGL function  |
Returns the most common value in a data set |
NEGBINOM.DIST function  |
Returns the negative binomial distribution |
NORM.DIST function  |
Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
NORM.INV function  |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
NORM.S.DIST function  |
Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
NORM.S.INV function  |
Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| PEARSON function | Returns the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient |
PERCENTILE.EXC function  |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, exclusive |
PERCENTILE.INC function  |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
PERCENTRANK.EXC function  |
Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, exclusive) of the data set |
PERCENTRANK.INC function  |
Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
| PERMUT function | Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects |
PERMUTATIONA function  |
Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects (with repetitions) that can be selected from the total objects |
PHI function  |
Returns the value of the density function for a standard normal distribution |
POISSON.DIST function  |
Returns the Poisson distribution |
| PROB function | Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits |
QUARTILE.EXC function  |
Returns the quartile of the data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, exclusive |
QUARTILE.INC function  |
Returns the quartile of a data set |
RANK.AVG function  |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
RANK.EQ function  |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
| RSQ function | Returns the square of the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient |
| SKEW function | Returns the skewness of a distribution |
SKEW.P function  |
Returns the skewness of a distribution based on a population: characterization of the degree of asymmetry of a distribution around its mean |
| SLOPE function | Returns the slope of the linear regression line |
| SMALL function | Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set |
| STANDARDIZE function | Returns a normalized value |
STDEV.P function  |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
STDEV.S function  |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
| STDEVA function | Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| STDEVPA function | Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| STEYX function | Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression |
T.DIST function  |
Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student tdistribution |
T.DIST.2T function  |
Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student tdistribution |
T.DIST.RT function  |
Returns the Student's t-distribution |
T.INV function  |
Returns the t-value of the Student's t-distribution as a function of the probability and the degrees of freedom |
T.INV.2T function  |
Returns the inverse of the Student's t-distribution |
T.TEST function  |
Returns the probability associated with a Student's t-test |
| TREND function | Returns values along with a linear trend |
| TRIMMEAN function | Returns the mean of the interior of a data set |
VAR.P function  |
Calculates variance based on the entire population |
VAR.S function  |
Estimates variance based on a sample |
| VARA function | Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| VARPA function | Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
WEIBULL.DIST function  |
Returns the Weibull distribution |
Z.TEST function  |
Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |
Engineering Functions
Engineering Functions are used to perform common engineering calculations. Information about the following functions is provided via support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| BESSELI function | Returns the modified Bessel function In(x) |
| BESSELJ function | Returns the Bessel function Jn(x) |
| BESSELK function | Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(x) |
| BESSELY function | Returns the Bessel function Yn(x) |
| BIN2DEC function | Converts a binary number to decimal |
| BIN2HEX function | Converts a binary number to hexadecimal |
| BIN2OCT function | Converts a binary number to octal |
BITAND function  |
Returns a 'Bitwise And' of two numbers |
BITLSHIFT function  |
Returns a value number shifted left by shift_amount bits |
BITOR function  |
Returns a bitwise OR of 2 numbers |
BITRSHIFT function  |
Returns a value number shifted right by shift_amount bits |
BITXOR function  |
Returns a bitwise 'Exclusive Or' of two numbers |
| COMPLEX function | Converts real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number |
| CONVERT function | Converts a number from one measurement system to another |
| DEC2BIN function | Converts a decimal number to binary |
| DEC2HEX function | Converts a decimal number to hexadecimal |
| DEC2OCT function | Converts a decimal number to octal |
| DELTA function | Tests whether two values are equal |
| ERF function | Returns the error function |
ERF.PRECISE function  |
Returns the error function |
| ERFC function | Returns the complementary error function |
ERFC.PRECISE function  |
Returns the complementary ERF function integrated between x and infinity |
| GESTEP function | Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value |
| HEX2BIN function | Converts a hexadecimal number to binary |
| HEX2DEC function | Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal |
| HEX2OCT function | Converts a hexadecimal number to octal |
| IMABS function | Returns the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number |
| IMAGINARY function | Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number |
| IMARGUMENT function | Returns the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians |
| IMCONJUGATE function | Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number |
| IMCOS function | Returns the cosine of a complex number |
IMCOSH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a complex number |
IMCOT function  |
Returns the cotangent of a complex number |
IMCSC function  |
Returns the cosecant of a complex number |
IMCSCH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of a complex number |
| IMDIV function | Returns the quotient of two complex numbers |
| IMEXP function | Returns the exponential of a complex number |
| IMLN function | Returns the natural logarithm of a complex number |
| IMLOG10 function | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number |
| IMLOG2 function | Returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number |
| IMPOWER function | Returns a complex number raised to an integer power |
| IMPRODUCT function | Returns the product of from 2 to 255 complex numbers |
| IMREAL function | Returns the real coefficient of a complex number |
IMSEC function  |
Returns the secant of a complex number |
IMSECH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic secant of a complex number |
| IMSIN function | Returns the sine of a complex number |
IMSINH function  |
Returns the hyperbolic sine of a complex number |
| IMSQRT function | Returns the square root of a complex number |
| IMSUB function | Returns the difference between two complex numbers |
| IMSUM function | Returns the sum of complex numbers |
IMTAN function  |
Returns the tangent of a complex number |
| OCT2BIN function | Converts an octal number to binary |
| OCT2DEC function | Converts an octal number to decimal |
| OCT2HEX function | Converts an octal number to hexadecimal |
Other Functions
Other functions groups, such as Cube, Information, Compatibility, & Web are also located at support.office.com (anonymous, 2020).


